
The end of the preceding neuron constitutes the synaptic bulb, while the modified area of the subsequent neuron forms the synaptic cleft. They are specialized areas where chemical information is passed from a neuron to another neuron or end effector organ, resulting in the generation of an action potential. These junctions are collectively known as synapses. Neurotransmitters are released from the end of the telodendria onto neighbouring axons, somata, dendrites, or end organs to propagate the message being transmitted. The end of the axon branches out into numerous projections called telodendria (s. The cells responsible for carrying out the myelination vary depending on whether the neurons are in the central nervous system (myelinated by oligodendrocytes) or in the peripheral nervous system (myelinated by Schwann cells). It has a diameter of 0.2 – 1.5 μm and conducts at a rate of 0.5 to 2.5 m/s. Unmyelinated fibers (type C/IV) are the smallest class of nerve fibers that carries pain, temperature and olfactory afferents.At 1 – 3 μm in diameter and a conduction velocity of 5 – 15 m/s, they are found in white rami and the fibers of CN III, CN VII, CN IX and CN X.
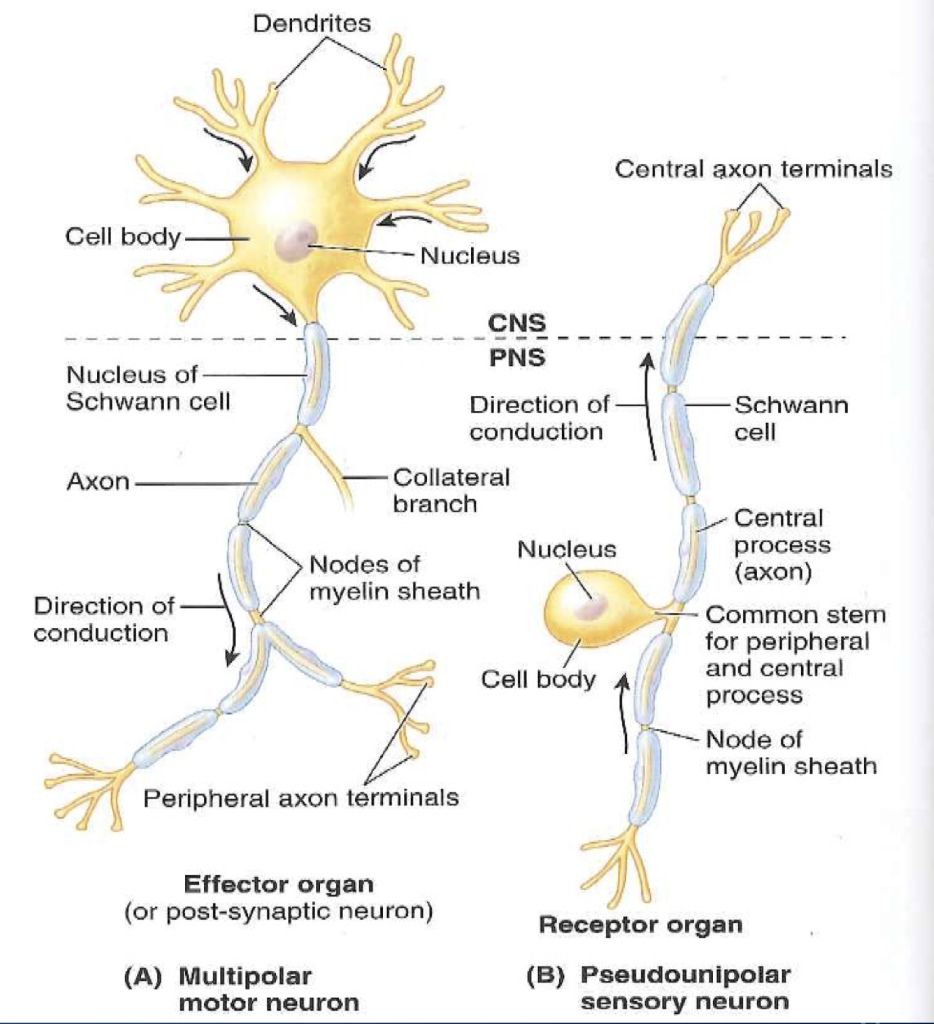
White ramus communicans (cranial view)Type B fibers are the smallest of the myelinated fibers. It will also cover briefly the histological layers of the central and peripheral nervous systems. This article will explain the histology of neurons, providing you with information about their structure, types, and clinical relevance. Peripheral nerves - epineurium, perineurium, endoneurium Myelinated (nodes of Ranvier) vs nonmyelinatedĬerebrum - molecular, external granular, external pyramidal, internal granular, internal pyramidal, multiform layersĬerebellum - molecular, Purkinje, granular layers Presynaptic terminal, synaptic cleft, neurotransmitter, postsynaptic terminalĬell body (soma), dendrites (covered with dendritic spines), axon, axon hillock.
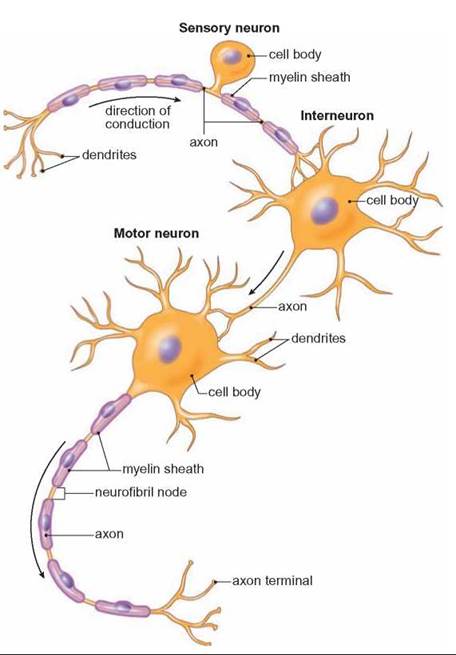
'top-down' information from the brain to the periphery, via efferent neurons (e.g.The cytology of a neuron facilitates the transmission of either: This laid the foundation for what has been referred to as the neuron doctrine.Ī neuron (nerve cell) is a specialized cell that conveys electrochemical impulses throughout the body. Subsequent research showed that each neuron is capable of operating independently. Prior to the late 19th century, neurons were viewed as collective functional units that formed a syncytium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
